 Gen info Gen info
- Etymology: Genus name Hypserpa derives from Greek words hypsos 'height' and herpo 'to creep', referring to the climbing habit. (8)
Botany
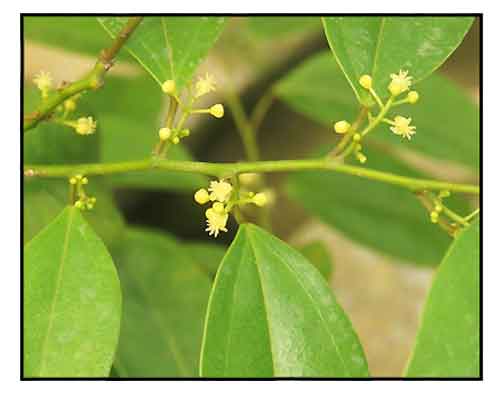
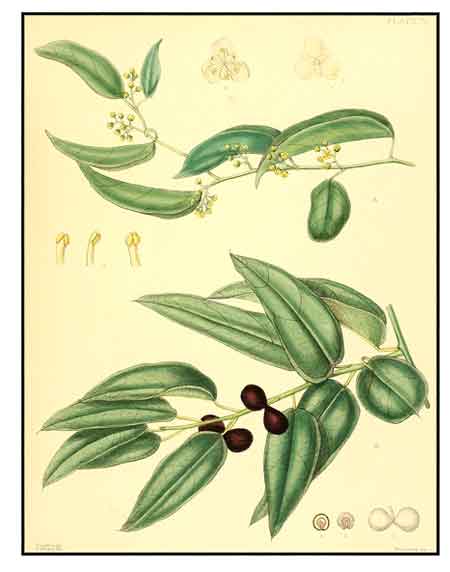
Hypserpa nitida is a woody vines. Branchlets sparsely to densely pubescent with yellowish hairs when young, glabrescent. Petiole 1-2 cm, pubescent or subglabrescent; leaf blade ovate, ovate-elliptic to oblong-elliptic, rarely elliptic or broadly elliptic, 4-10(-12) × 1.5-5(-7) cm, papery to leathery, both surfaces usually glabrous, rarely pubescent along nerves, adaxially glossy, base rounded to broadly cuneate, apex acuminate, mucronate, or slightly obtuse with a finely mucronate acumen, palmately 3-veined. Male inflorescences usually only few flowered, cymose to paniculate, 1-2 cm, rarely longer and more flowered, pubescent. Male flowers: sepals 7-11, outer sepals minute and bracteolelike, 0.5-0.8 mm, puberulent outside, innermost 4 or 5 broadly obovate or ovate to ovate-rotund, 1.5-2.5 mm, ciliate; petals 4 or 5, subobovate, 1-1.2 mm; stamens 5-10, free above or connate only at base, 1-1.5 mm. Female flowers: sepals and petals as in male; carpels 2; ovary semiglobose or subelliptic, 0.8-1 mm, glabrous. Drupes subglobose, slightly compressed, yellow or orangish red when mature; endocarp obovate, 5-6 mm. (Flora of China)
 Distribution Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
- Also native to Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China, Hainan, India, Laos, Malaya, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Thailand. (2)
- Grows primarily in wet tropical biome.
- Forests and forest margins, up to 2000 m elevation.
Constituents
- Study isolated two new alkaloids, hypserpanines A and B (1, 11), together with eleven known compounds, phenolbetain (2), acutumine (3), acutumidine (4), dechloroacutumine (5), dauricumine (6), dauricumidine (7), pronuciferine (8), glaziovine (9), S-reticuline (10), magnoflorine (12) and laurifoline(13). (see study below) (3)
- Roots contain alkaloids limacine and fanchinoline.
(5)
- Contains glaucine (C18H19NO3), an isoquinoline alkaloid.
(6)
Properties
- Study suggested anti-hepatitis B property.
Parts used
Roots, leaves, whole plant.
Uses
Folkloric
- No reported folkloric medicinal use in the Philippines.
- Roots contain alkaloids limacine and fanchinoline, which are used medicinally.
(5)
- In Chinese medicine, used for cooling blood and stopping bleeding, anti-inflammation and diuresis. Use for treatment of hemoptysis, hematemesis, hematochezia, and traumatic bleeding. Decoction for oral use 6-12 gm per doses. For external use, ground into powder and applied to affected areas. (7) Leaves applied to wounds. (8)
Others
- Fiber / Cordage: Stems used for tying or making rough rope. In the Philippines, bast fiber made into bow string. (1)
Studies
• Anti-Hepatitis B / Alkaloids: Study isolated two new alkaloids, hypserpanines A and B (1, 11), together with eleven known compounds. All the isolated alkaloids were evaluated for anti-HBV activity in vitro using HBV transfected HepG2.2.15 cell line. The most active compound, dauricumidine (7), exhibited an IC50 of 0.450 mM (SI=4.13) on hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HbsAg) secretion of the Hep G2.2.15 cell line. (see constituents above) (3)
• Herbal Mixture for Chronic Prostatitis / Invention: Hypserpa nitida is one of ten herbal constituents in a herbal Chinese invention for treating chronic prostatitis, which is purported to match antibiotics. (4)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()




 Distribution
Distribution