| General
info
One of the most ancient
trees in existence, ginkgo biloba trees can live as long as 1000 years.
its leaves are among the most extensively studied botanicals in use
today. Unilke most medicinal herbs, ginkgo is not usually used in its
crude state but in a standardized ginkgo biloba extract (GBE). In France
and Germany, it continues to be the top ranked prescribed medicine.
Botany
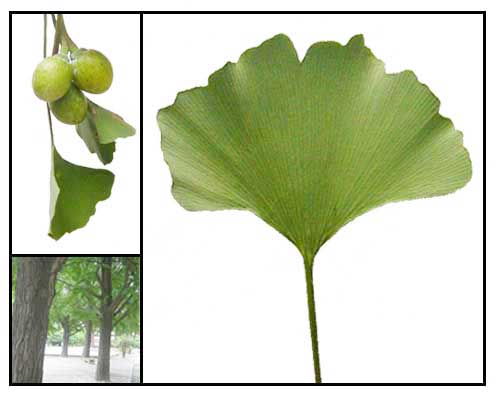
Tall tree with a resinous
trunk that can grown as high as 120 feet. Leaves are fan-shaped, long
stalked. Flowers are in clusters, the male smaller than the female.
The fruit is drupelike and long-stalked with a fleshy foul-smelling
pulp that encloses an oval-pointed seed 1-2 cm long.
Distribution
Native to China.
Planted in the Baguio area, but with limited survival.
Chemical constituents
and properties
• Two main constituests
are responsible for its medicinal effects: terpene lactones and ginkgo
flavone glycosides.
• About 40 different flavonoids have been isolated, including:
ginkgetin, bilogetin and sciadopitysin.
• Terpenes isolated include ginkgolides (ginkgolides A, B, and
C with bilobalide) and diterpenes
• Flavone glycosides, including quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin,
have antioxidant properties.
• Terpenoids (ginkgolides) improve circulation.
• Bilobalides have neuroprotective properties.
• It alters vasoregulation, modulates neurotransmitter and receptor
activity and inhibits PAF (platelet activating factor).
Concerns
PREOPERATIVE SURGICAL: The effect on PAF
and platelet aggregation may contribute to perioperative bleeding. Ginkgo
use should be discontinued at least 16 hours before surgery.
Some Ginkgo products may contain a neurotoxin (Ginkgo toxin) that might
increase the risk of seizures
Parts
used and preparation
Leaves, flowering
spikes, roots.
Uses
Folkloric
and modern day uses
• Chinese
medicine has used the leaf and seed for centuries. Used for asthma,
digestive disorders.
• In this new age of antioxidants, glycosides and flavonoids,
Ginkgo is promoted to treat Alzheimer's disease and dementia, improve
memory and cognitive function, cerebral and peripheral blood flow (claudication),
tinnitus and vertigo.
• Erectile dysfunction:
Because of its effect on circulation, it has become an ingredient in
many Herbal Viagra concoctions to increase the blood flow to the genitals
• Memory enhancement:
The largest and longest clinical trial concluded ti provides no measurable
benefit in memory or related cognitive function to adults with healthy
cognitive function.
Others
• Fruits are fermented in vats or water to remove
the malodorous pulp. Nuts are then washed, boiled shelled or unshelled
or sun-dried. The cooked soft inner kernel is edible with a pleasant
mild Swiss-cheese flavor, consumed as an appetizer and believed to promote
digestion and the counter the effects of excessive drinking.
• Ginkgo nuts, considered an oriental delicacy (silverfruits),
are consumed in Chinese and Japanese rituals, feasts and weddings.
• When gathered, the fruits are either fermented in vats or water
to remove the pulp, with its stinking odour suggestive of rancid butter,
or buried to hasten the pulp’s decay. They are then washed and
dried in the sun. Roasting or boiling the nuts, either shelled or in
the shell, completes the task of getting rid of the unpleasant taste.
The soft, inner kernel, when cooked, is edible, with a pleasant flavour
similar to mild Swiss cheese - it is said to promote digestion and diminish
the effects of too much drinking. Ginkgo nuts have a ritual significance
in China and Japan, where they are consumed at feasts and weddings as
an oriental delicacy called "silverfruits".
• Leaves are inserted between book pages to prevent insect infestation
and damage.
Studies
• Hematologic Effects / Platelet Activating Factor Binding Inhibition / Fibrinogen Lowering: Terpene lactones inhibit the binding of PAF (platelet-activating
factor) to membrane receptors. (2) Ginkgo biloba extracts may lower serum fibrinogen concentration.
• Antioxidant: In rabbit studies, Ginkgo biloba extracts demonstrated
antioxidant properties with reduced superoxide release.
• Raynaud's Disease: The
use of Ginkgo biloba in Raynaud’s disease: a double-blind placebo-controlled
trial : GB
may be effective in reducing number of Raynaud's attacks per week.
• Dementia Studies / Not Effective: In this study, G biloba at 120 mg twice daily was not effective in reducing either the overall incidence rate of dementia or Alzheimer's Dementia incidence in elderly individuals with normal cogniztion or those with MCI.
.
Availability
Wildcrafted.
Commercial available as standardized Ginkgo biloba extracts (GBE) which
is prepared from dried green leaves.
|


![]()

