
Family • Menyanthaceae
Pusong-lutang
Nymphoides hydrophyllum (Lour.) Kuntze
CRESTED FLOATING HEART
Ci zhong xing cai
| Scientific names | Common names |
| Limnanthemum cristatum (Roxb.) Griseb. | Lolokisen (Ilk.) |
| Limnanthemum hydrophyllum (Lour.) Griseb. | Pusong-lutang (Tag.) |
| Limnanthemum taquetii H.Lév. | Crested floating heart (Engl.) |
| Menyanthes cristata Roxb. | Floating heart (Engl.) |
| Menyanthes hydrophyllum Lour. | Snow flake (Engl.) |
| Menyanthes sinarica Buch.-Ham. ex Steud. | White water snowflake (Engl.) |
| Nymphoides cristata (Roxb.) Kuntze | |
| Nymphoides hydrophyllum (Lour.) Kuntze | |
| Villarsia cristata (Roxb.) Spreng. | |
| Villarsia hydrophyllum (Lour.) Roem. & Schult. | |
| Nymphoides cristata (Roxb.) Kuntze is a synonym of Nymphoides hydrophyllum. | |
| Nymphoides hydrophyllum (Lour.) Kuntze is an accepted species. KEW: Plants of the World Online | |
| Other vernacular names |
| BANGLADESH: Jai chirata, Chand mala. |
| CHINESE: Ci zhong xing cai. |
| HINDI: Hinambala. |
| INDIA: Pan-seuli, Panikola (Assamese); Cheruthettambel, Neythel (Malayalam); Kumudini. |
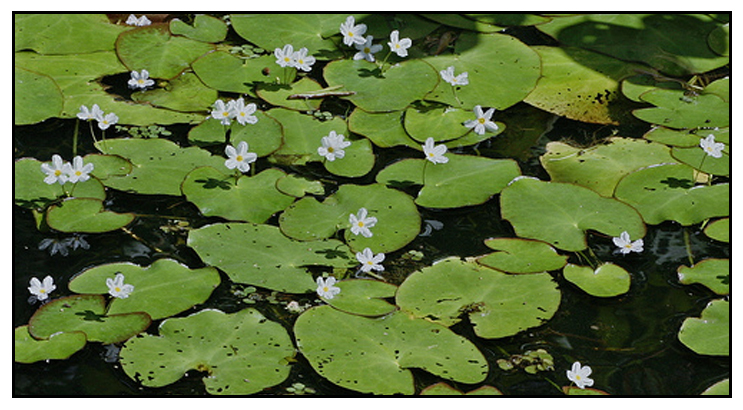
Botany • Stems 10-30 cm, rooting from nodes. Leaves few per node; petiole 4-10 cm, slender; leaf blade cordate, 1-6 × 1-4(-5) cm, submembranous, veins indistinct. Flowers 2-10 per node, 5merous, homostylous. Pedicel 2-6 cm, slender. Calyx 4-5 mm, lobed to near base; lobes narrowly oblong, apex acute. Corolla white, campanulate, 7-8 mm, lobed to middle, tube 4-5 mm; lobes 3-4 mm, margin laciniate, apex emarginate. Filaments absent; anthers triangular, ca. 1 mm. Style very short. Capsules globose, ca. 3 mm in diam., 6-10- seeded. Seeds brown, globose, ca. 1 mm in diam.; seed coat spinescent. (Flora of China)
- In a study for various antioxidant substances, Nymphoides cristata yielded polyphenols 3.82 ± 1.02 mg GAE/g DW, flavonoids 23.28 ± 0.54 mg QUE/g DW, flavonols 6.71 ± 0.44 mg QUE/g DW. Anthocyanidins were not detected. (6) - In a study for flavonols content in acidic hydrolysates, N. cristata yielded in quercetin 116.53 ± 26.66 µg/g DW, myricetin 1099.85 ± 37.03 µg/g DW, morin 3869.54 ± 213.27 µg/g DW, and kaempferol 107.41 ± 5.35 µg/g DW. (6) Properties Studies Availability |
Updated April 2025 / May 2022 / June 2018 / December 2013
![]()
 |
PHOTOS / ILLUSTRATIONS |
| IMAGE SOURCE: Crested Floatingheart (Nymphoides cristata) -- Mary Keim / Sept 19, 2011 / Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-share alike 2.0 / Click on photo or link to go to source page / flickr |
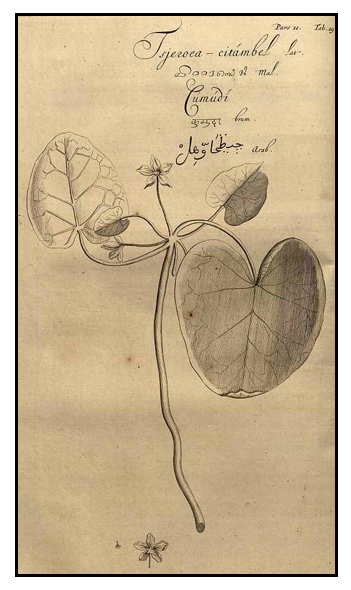
| OTHER IMAGE SOURCE: / Illustration / Nymphoides cristata (Roxb.) Kuntze [as Limnanthemum cristatum (Roxb.) Griseb.] [4630-705250-123342] / Rheede tot Drakestein, Hendrik van, Hortus Indicus Malabaricus, vol. 11: t. 29 (1692) / PlantIllustrations.org |
| OTHER IMAGE SOURCE: Nymphoides hydrophylla / Vengolis / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International /Image modified / Click on image or link to go to source page / Wikimedia Commons |
| OTHER IMAGE SOURCE: Nymphoides hydrophylla / Self-Made / CC BY-SA 3.0 Unported / Click on image or link to go to source page / / Wikipedia |
Additional
Sources and Suggested Readings |
• |
DOI: It is not uncommon for links on studies/sources to change. Copying and pasting the information on the search window or using the DOI (if available) will often redirect to the new link page. (Citing and Using a (DOI) Digital Object Identifier) |
| Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â List of Understudied Philippine Medicinal Plants |
| Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â New plant names needed The compilation now numbers over 1,500 medicinal plants. While I believe there are hundreds more that can be added to the collection, they are becoming more difficult to find. If you have a plant to suggest for inclusion, native or introduced, please email the info: scientific name (most helpful), local plant name (if known), any known folkloric medicinal use, and, if possible, a photo. Your help will be greatly appreciated. |
• |
 |


 Gen info
Gen info
