|
 Gen info Gen info
- Acalypha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole genus of the subtribe Acalyphinae. It is one of the largest euphorb genera, with about 450-462 species.
-
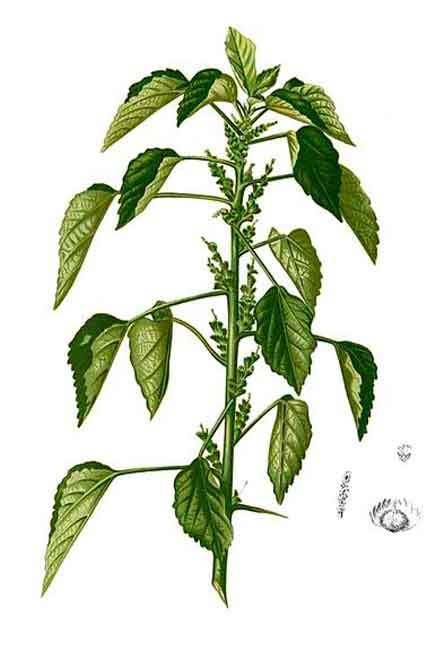
Acalypha indica is an herbaceous annual that has catkin-like inflorescences with cup-shaped involucres surrounding the minute flowers.
-
It is mainly known for its effect on domestic cats, which react strongly to the plant root. The chemicals that attract cats are iridoid compounds isodihydronepetalactone and isoiridomyrmecin. (see study below) (64)
- Etymology:
The genus name Acalypha derives from ancient Greek akaluphe meaning "nettle". An alternative form is akalephe, "nettle-like leaves". Specific epithet indica is Latin for "of India", referring to the plant's native origin, although it is now widely grown elsewhere.
Botany
Maraotong is an erect, simple or branched, slightly
hairy annual herb, growing to a height of 30 to 80 centimeters. Leaves are ovate.
3 to 6 centimeters long, shorter than the long stalks, with toothed margins.
Flowers are sessile, greenish, borne on numerous, lax, erect axillary spikes.
The male flowers are very small, clustered near the summit. Female flowers
are solitary and scattered, each with a large and leafy bract, 5 to 6 millimeters long.
Capsules are 2 millimeters long and concealed by the enlarged bract, often containing only one seed. Seed is ovoid and smooth.
An erect annual herb that can be easily distinguished by the cup-shaped involucre that surrounds the small flowers in the catkin-like inflorescence. It can grow up to 1.2 m (3.9 ft) tall in favorable circumstances, but is usually smaller. The leaves are broad ovate, 1.2 cm–6.5 cm × 1 cm–4 cm (0.47 in–2.56 in × 0.39 in–1.57 in). The leaf base is rounded to shortly attenuate. The leaf margin is basally 5-nerved and is crenate-serrate with an acute or obtuse apex. The petiole is 1.5–5.5 cm (0.59–2.17 in) long. Flower spikes are axillary, 2.5–6 cm (0.98–2.36 in) long, monoecious, with a rachis terminating in a triradiate hood. Tiny male flowers are white-green, located on the upper part of the flower spikes, and are ebracteate, minute, and clustered with vermiculiform anthers. The pollens are roughly round and approximately 10–12 microns in diameter. Green female flowers are located lower on the spikes, and are subtended by 3–7 mm (0.12–0.28 in) long suborbicular-cuneiform, many-nerved, toothed bracts that are foliaceous. The ovary is hispid, 3-lobed. Styles are 3, each 2-fid. Capsules are hispid, 3-valved and concealed by a bract. The stem is striate (longitudinally ribbed) and pubescent. The fruit is 1.5–2 mm (0.059–0.079 in), 3-lobed, tuberculate and pubescent. (53)
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
A common weed in and about towns, in thickets and waste places throughout
the Philippines.
- Also found in tropical Africa and Asia, through Malaya and Polynesia.
 Constituents Constituents
- Contains an alkaloid, acalyphine.
- Major phytochemicals identified are acalyphine, cyanogenic glycoside, inositol, resin, triaetomamine and volatile oils.
- Phytochemical screening of leaves yielded alkaloids, tannins, steroids, saponins, flavonoids, glycosides, and phenolic compounds.
(see study below) (23)
- Study for fatty acids yielded eicosatrienoic acid methyl ester (35.47 ± 2.40%), hexatriacontane (9.56 ± 0.71%), 2,6,10 trimethyl undecatriene (8.69 ± 0.59%) and trifluoroacetic acid, n-heptadecyl ester (8.92 ± 0.52%).
The highest volatile oil component was phytol (38.85%). Flavonoids from AI leaf were naringin (highest), quercitrin, hesperitin and kaempferol. (33)
- In a proximate analysis of dried samples of root, leaves, stem and whole plant, leaves yielded highest moisture (9.49%), ash (12.83%) and protein (23.98%).
Roots yielded highest carbohydrate (76.33%), crude fiber (42.05%), and gross energy (1453.94 kJ) content. Triterpenes were present in ail samples analyzed. (40)
 - Phytochemical screening of dried roots yielded flavonoids ++, triterpenes + and steroid +. Dried stems yielded flavonoids +, triterpenes ++, steroids ++. Dried leaves yielded flavonoids +, tannins +, triterpenes +++, steroid +++, and dried whole plant yielded alkaloids +, flavonoids +, tannins +, triterpenes +++, and steroid+++.
(40) - Phytochemical screening of dried roots yielded flavonoids ++, triterpenes + and steroid +. Dried stems yielded flavonoids +, triterpenes ++, steroids ++. Dried leaves yielded flavonoids +, tannins +, triterpenes +++, steroid +++, and dried whole plant yielded alkaloids +, flavonoids +, tannins +, triterpenes +++, and steroid+++.
(40)
- Phytochemical analysis of root methanolic extract showed rich content of phenols (70.92 mg gallic acid/g) and flavonoids (16.01 mg rutin/g).
HR-LC-MS and GC-MS analysis identified 104 and 14 phytochemical compounds, respectively. Predominant phytomolecules were ramipril glucuronide (1.563%), antimycin A (1.324%), swietenine (1.134%), quinone (1.152%), oxprenolol (1.118%), choline (0.847%), bumetanide (0.847%) and fenofibrate (0.711%). (see study below) (54)
Properties
- Anthelmintic, cathartic, diuretic, emetic, expectorant, laxative.
- Roots considered cathartic and laxative.
- Studies have suggested anti-inflammatory, anti-malarial, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, neuroprotective, gastroprotective, mosquito larvicidal, anticancer, membrane stabilizing, hepatoprotective, leptin and alpha glucosidase inhibitory, wound healing properties.
Toxicity
- Some constituents cause intense dark chocolate-brown discoloration of blood and gastrointestinal irritation in rabbits. Ingestion of herbal medicines containing Acalypha indica may cause hemolysis in patients with G6PD (glucose-6-phosphatase dehydrogenase) deficiency.
• Poisoning / Methemoglobenemia: (See study below) (55)
Parts utilized
Roots, leaves, sap.
Uses
Edibility
- In India, as famine food, leaves eaten as vegetable.
- In West Africa, leaves are cooked and eaten as vegetable. (Caution advised since plant is reported to contain several alkaloids as well as hydrocyanic acid.)
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, decoction of leaves used for dysentery.
- Juice of the root and leaves given to children as expectorant and emetic.
- The leaves, in decoction or powdered form, is used as a laxative.
- For constipation, an anal suppository of the bruised leaves helps relax
the constricted sphincter ani muscle.
- Leaves mixed with garlic used as anthelmintic.
- Leaves mixed with common salt applied to scabies.
- Leaves mixed with tumeric used for acne.
- Poultice of bruised leaves used for syphilitic ulcers, to maggot-eaten
sores and as emollient to snake bites.
- Powdered dried leaves used for bed sores.
- Leaves used for treatment of insomnia.
- Leaves applied to pustules and insect bites.
- Juice of fresh leaves, mixed with oil or lime, used for rheumatic complaints.
- Decoction of leaves used as instillation for earaches and for periauricular
poultice or compress
- Root, bruised in water, used as cathartic.
- Bruised leaves used as "suppository" in constipation, assumed to work through decrease of the sphincter ani contraction.
- In Indian pharmacopoeia, used as an expectorant.
Also used for the prevention and reversal of atherosclerotic disease. Used for pneumonia, asthma and rheumatism.
- In Tamil Nadu, India, the Paliyar tribes of Shenbagathope use the entire
plant for bronchitis, a decoction of the herb for tooth- and earaches
and paste of the leaves applied to burns.
- In traditional Tamil Siddha medicine, plant believed to rejuvenate the body.
- In Madagascar, crushed plants used for skin parasites.
- In Mauritius, sap from crushed leaves mixed with salt used for treatment of scabies.
- In Seychelles and Reunion, root infusion or decoction use for treatment of asthma. Root decoction used for stomachaches and intestinal worms.
- Leaf sap taken as emetic.
- In Siddha medicine, Charu,
a herbal formulation made from fresh leaves, is used for various fungal skin infections. In Siddha system of medicine, leaves, roots, stalk and flowers are used for its medicinal properties. Leaf powder used for respiratory diseases; leaf juice mixed with Neem oil is applied to inner part of the child's tongue with the help of a quill to induce vomiting or act as expectorant. Whole plant is used for asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and rheumatism. (60)
Others
- Dye: Dye extracted from eaves can be used for coloring textiles. Different shades of color can be obtained using chemical and natural mordants. The dye extract has shown good antibacterial and antifungal activity. (34)
- Fodder: In north-eastern Africa, A. indica is browsed by sheep and goats.
Studies
• Post-Coital Infertility Activity:
Petroleum ether and ethanol extracts of A. indica were found
to be effective in causing significant anti-implantation activity. (1)
• Flavonoids: Four known kaempferol glycosides–mauritianin,
clitorin, nicotiflorin and biorobin were isolated from the flowers and
leaves of A. indica. (2)
• Fatty Acids / Essential Oils / Flavonoids: Studies yielded fatty acids (eicosatrienoic acid methyl
ester, hexatriacontaine, trimethyl undecatriene and trifluoroacetic
acid), volatile essential oil (phytol), and flavonoids (naringing, quercitrin,
hesperitin and kaempferol) -- most of the identified components having
their own medicinal properties. (3)
• Antibacterial: (1) Study have shown it to possess antibacterial activity
against Aeromonas hydrophylla and Bacillus cereus. (2) All extracts of leaves of Acalypha indica exhibited antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus, S. epidermis, B. cereus, Strep faecalis). Among gram-negative bacterial only P. aeruginosa was susceptible to the extracts.
• Antifungal / Antimicrobial: (1) Study of fresh, dried and powdered samples of leaf,
stem and root of Acalypha indica showed activity against Candida albicans,
Aspergillus niger and E. coli. An active compound showed more activity
than clotrimazole. (2) Study concludes the plant has potential antifungal properties providing a scientific basis for utilization of the plant for treatment of antifungal infections. Results of study were negative for antibacterial activity against E coli and S aureus.
• Antimalarial / Leaves: Results of leaf extract of A. indica show promising
larvicidal and ovicidal activity against malaria vector A. stephensi. (5)
•Neuroprotective / Neurotherapeutic: Results of water extract study showed A indica has neuroprotective and neurotherapeutic effects ex vivo on m. gastrocnemius frog. (7)
• Antioxidant: Ethanol and aqueous extract of root of A indica showed nitric oxide scavenging activity in a dose-dependent manner. (8)
• Antibacterial / Antioxidant: Study of Acalypha indica and Ocimum basilicum showed antibacterial activity against E coli, K pneumonia, S aureus, P aeruginosa and Proteus sp, the ethanol more effective than the acetone extract. (9)
• Wound Healing / Antimicrobial: Study showed the water extracts of Azadirachta indica and Acalypha indica were more effective than the acetone extracts particularly on pseudomonas sp. Results suggest a potential for use in wound infections. (10) Study evaluated the antimicrobial activity of water and acetone extracts of A. indica leaves against two strains of human pathogenic bacteria in infected wounds i.e., Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Results showed a water extract to have highest antibacterial activity to the acetone extract. (52)
• Antidiabetic: Study of methanol and acetone extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rat model showed dose-dependent antidiabetic activity attributed to an increased uptake of glucose at the tissue level or by an increase in pancreatic beta cell function or due to inhibition of intestinal absorption of glucose. (12)
• Vasoconstrictor Activity: Study showed the petroleum ether extract exhibited better vasoconstrictor activity against blood vessels of frog comparable to the reference drug adrenaline. Results provide support for use of the extract in treating disorders of headache and migraines, and for diuretic and alexeteric effects. (13)
• Antimicrobial: Study evaluating the antimicrobial activity of different extracts of A. indica showed antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria was more pronounced in water and ethanol extracts and antifungal activity significant with the chloroform extract. (14) Study evaluated various leaf extracts for antimicrobial activity against various bacterial strains. An acetone extract showed maximum zone of inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis; an aqueous extract showed maximum inhibition against E. coli, B. subtilis and S. aureus. Antimicrobial activity was attributed to phytocompounds like alkaloids, tannins, saponins, steroids and proteins. (41)
• Anthelmintic / Leaves / Roots: Study evaluated an ethanol extract of leaves for anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma. Results showed significant anthelmintic activity at 100 mg/mL. (15) Study evaluated the anthelmintic potential of crude ethanolic extract of roots using Pheretima posthuma as test worm. Results showed significant anthelmintic activity when compared to reference drug Albendazole. (30)
• Improved Hippocampal Cell Viability in Hypoxic Condition / Stroke Benefits: Study showed a root extract of Acalypha indica is able to improved rat hippocampal cell viability and endogenous BDNF (Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor) levels in hypoxic condition. (17)
• Gastroprotective: Study evaluated the gastroprotective effect of leaves and roots of A. indica on rats with peptic ulcers induced by physical and chemical agents. Results showed the ethanol root extract with dose-dependent ulcer protective effect on peptic ulcers induced by physical and chemical agents. (18)
• Nerve Protection: Study evaluated nerve protection of A. indica extract on nerve paralysis induced by subcutaneous injection of pancuronium bromide on frog's back. Results showed comparable protective and treatment effect on the the nerves as piracetam. (19)
• Anti-Arthritic / Root: Study evaluate a methanol extract of root in in vitro models for potential in inhibition of protein denaturation, proteinase inhibitory action and antihyaluronidase activity. A dose-dependent inhibition was showed in all three models. Results showed very good anti-arthritic activity. Â (20)
• Antioxidant / Anticancer / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated aerial parts for antioxidant, anticancer activity, and cytotoxicity. Results showed a non-cytotoxic response against Vero cells, anticancer activity against NCIH187-Small Cell Lung Cancer, and significant antioxidant activities. (21)
• Toxicity Study: Study evaluated acute and subacute toxicity of the ethanolic extract of A. indica on male Wistar rats. Results showed no significant signs of toxicity at the dose levels used in the study (100 - 500 mg/kbw) and suggests safety for alternative use for various infections. (22)
• Antibacterial / Leaves: Study of ethanol extract showed activity against Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. The good antibacterial activity is less than standard erythromycin. (see constituents above) (23) Study evaluated the antibacterial activity of A. indica against three strains of human pathogenic bacteria viz., Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia
• Anti-Inflammatory / Membrane Stabilization / Leaves: Study evaluated the methanolic extract of leaves for anti-inflammatory activity in HRBC membrane stabilization. Results showed significant dose dependent inhibition of erythrocyte hemolysis induced by hypotonic solution. Diclofenac sodium was used as reference drug. (24)
• Antihyperlipidemic / Leaves: Study evaluated the antihyperlipidemic activity of aqueous extracts of A. indica in Wistar albino rats with hyperlipidemia induced by an atherogenic diet. Results showed improvement of lipid profile and improvement of atherogenic index with decrease in serum TC, TG, LDL-C and increase in HDL-C. (25)
• Nanoparticles / Cytotoxicity / Human Breast Cancer Cells: Study evaluated the in-vitro cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles against MDA-MB-231, human breast cancer cells. Results showed the plant derived nanoparticles exhibited significant cytotoxic effects with apoptotic features confirmed through caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation assays. (26)
• Hepatoprotective / Acetaminophen Induced Hepatotoxicity: An ethanol extract of leaves investigated against acetaminophen-induced hepatic damage showed hepatoprotective action through antioxidant effect. (27)
• Antibacterial / Leaves and Roots: Study evaluated the antibacterial activity of extracts of leaves, roots, and stems of A. indica against three strains of human pathogenic bacteria viz., Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia. The ethyl acetate extract of leaves and roots inhibited growth of all three selected bacterial species. (28)
• CNS Depressant Activity / Leaves and Roots: Study investigated the methanol extract of leaves of Acalypha indica in Swiss albino mice for central nervous system activity. Results showed CNS depressant activity. (29)
• Anti-Dermatophytic Activity / Leaves: Study investigated ethanolic, ethyl acetate and hexane leaf extracts of Azadirachta indica and Acalypha indica against dermatophytes (Trichophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, Microsporum gypseum and Trichophyton tonsurans).The ethanolic and EA extracts inhibited all the isolates. Azadirachta indica showed more activity than Acalypha indica. (31)
• Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles / Leaves: Aqueous leaf extract of A. indica was used to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles. Zinc oxide nanoparticles have significant applications in the field of medicine, pigment electronics, spintronics, and piezoelectricity. The green synthesis and biogenic invention of zinc oxide nanoparticle is an ecofriendly option that avoids conventional energy sources and harmful chemicals. (32)
• Hepatoprotective / Roots / Potentiating Effect of Piperine: Study showed roots of Acalypha indica exert a protective effect against CCl4 and Rifampicin-Isonazid induced hepatotoxicity. Results also show that piperine has a dose dependent potentiating effect on the hepatoprotective activity of A. indica. Piperine has been reported to enhance the bioavailability of some drugs by a non-specific and non-competitive inhibition of metabolic enzymes. (34)
• Urolithiasis Benefits / Biopotency on Membrane Bound Enzymes and Marker Enzymes: Study evaluated an ethanolic extract for its biopotency on membrane bound enzymes and marker enzymes in urolithiasis in male wistar albino rats. Results suggest AI can play a role in the prevention of disorders associated with kidney stone formation. (35)
• Mosquito Repellent / Larvicidal / Leaves: Study evaluated various leaf extracts and solvents for larvicidal, oviposition deterrent and repellent activities against mosquitoes Aedes aegypti, Anopheles stephensi, and Culex quinquefasciatus. Results showed A. indica contain larvicidal, oviposition deterrent and repellent compounds in its leaves, suggesting a potential ecofriendly candidate against mosquitoes. (36)
• Herbal Syrup for Antibiotic Resistant Klebsiella pneumonia UTI: In-vitro study evaluated the effect of herbal syrup of plant extract against ESBL (extended spectrum ß-lactamase) producing Klebsiella pneumonia causing urinary tract infections. Crude water extracts exhibited an antibiotic potential against multidrug resistant ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumonia UTIs from ICU patients. (37)
• Herbal Soap for Wound Healing: Soap made from extracted Kalipipi Acalypha indica was effective in healing wounds. Results suggest a potential alternative to commercial products—economical, user-friendly and highly effective. (38)
• Antibacterial / Leaves: GC-MS analysis of leaves yielded alkaloids, tannins, steroids, saponins, flavonoids, glycosides, and phenolic compounds. A methanolic extract showed activity against Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. (42)
• Antiplasmodial: Study evaluated leaf, stem, root, and flower extracts of A. aspera, A. indica, J. glandulifera and P. amarus for antiplasmodial activity against Plasmodium falciparum. The stem extract of A. indica showed excellent antiplasmodial activity (IC50=43.81 µg/mL). In vitro antiplasmodial activity may be due to the presence of alkaloids, phenols, flavonols, glycosides, saponins, triterpenoids, proteins and tannins in the ethanolic extract of tested plants. (43)
• Mosquito Larvicidal / Synergism with A. aspera: Study evaluated the biologic activities of methanol extracts of Acalypha indica and Achyranthes aspera leaves individually and in combination as botanical insecticides against 4th instar Ae. aegypti. The most effective larvicide was the combined extract of A. indica and A. aspera. LC50 for 1st and 4th instars was 207 ppm and 277 ppm, respectively. Both were 30% lower than for both extracts alone.. Combined extract was also the most effective pupicide, with LC50 of 326 ppm. (44)
• Cytotoxicity / Breast Cancer Cell Line / Leaves: Study evaluated the cytotoxic activity of a hexane leaf crude extract of Acalypha indica on MCF-7 cell lines by MTT. A 50 µg/ml concentration showed maximum inhibitory effect with IC50 of 54.75 compared to cisplatin at 93.11. (46)
• Anti-Psoriasis / Leaves:In vitro study evaluated the anti-psoriatic activity of an aqueous extract using AA431 and B16-F10 cell lines. Fluorescence studies showed 80% cell death and 75% apoptosis in both cell lines. Result suggests potential of the leaf extract as an anti-psoriatic agent. (47)
• Antimicrobial: Study evaluated various extracts of Acalypha indica for antimicrobial potential. Results showed crude extracts of stem bark and leaves showed antimicrobial activities against pathogenic microbes. Methanol and chloroform extracts showed good antifungal activity against Candida albicans. (48)
• Postprandial Antihyperglycemic / Antioxidant / Stem: Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors control postprandial hyperglycemia by preventing the sharp rise in blood glucose after ingestion of a carbohydrate-rich meal in T2DM. Study evaluated the postprandial antihyperglycemic potential of methanolic extract of stem of A. indica in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Results showed 69.10 and 80.35% blood glucose lowering effect in maltose and sucrose loaded diabetic rats via inhibition of α-glucosidase enzyme. The extract also improved antioxidant status and recovered the damage induced by streptozotocin. (49)
• Antiepileptic / Leaves: Study evaluated the anticonvulsant activity of methanolic extract of A. indica in Feel3 induced epilepsy in Sprague Dawley rats. Results showed significant decrease in duration of tonic hind limb extension suggesting anticonvulsant effect. (50)
• Hepatoprotective Against Hypoxia / Combination of A. indica and Centella asiatica: Study evaluated the combination of A. indica and Centella asiatic for hepatoprotective activity against hypoxia. Results showed one of the AI and CA combination showed significant protective effect against hypoxia in the liver (p<0.001) but not in the plasma. (51)
• Free Radical Scavenging / Anti-Inflammatory / Roots: In vitro and in vivo studies evaluated Acalypha root methanolic extract for free radical scavenging and anti-inflammatory properties. In vitro studies showed the extract scavenges DPPH and hydroxyl radicals in a concentration dependent manner (10-50 µg/mL). In vitro antioxidant activity was comparable to ascorbic acid. Extract pre-treatment significantly (p<0.05) decreased edema volume in carrageenan induced localized inflammation in rats. The extract attenuated carrageenan-induced neutrophil infiltrations and vascular dilation in paw tissues. (see constituents above) (54)
• Poisoning / Methemoglobinemia: Acute hemolysis has been recorded following ingestion of the plant by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)-deficient patients. Study reports on accumulated date from eight patients, mostly male, median age of 61.5. The plant was ground for fresh juice or boiled before consuming. All patients presented with dark urine, most had jaundice and fever, and all reported hemolysis. Seven of eight were diagnosed with methemoglobinemia, methemboglobin level was confirmed in five with highest level of 23.9%. Symptoms usually occurred within 24 hours of last ingested dose. One of eight patients died. Hemolysis, methemoglobinemia, and preexisting disease might have contributed to the deaths. Treatment is supportive case. (55)
• Antibacterial against Porphyromona gingivalis: Among major periodontal pathogens, P. gingivalis is one of the prime etiologic agents in the pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal disease. Study evaluated the antimicrobial efficacy of A. indica plant against P. gingivalis. The n-hexane extract showed best antibacterial potency at 200 mg/ml against P. gingivalis, which is compared to gold standard chlorhexidine and MIC of 150 mg/ml. Results suggest potential for utilization as antimicrobial against P. gingivalis and periodontal disease. (56)
• Antihyperglycemic / Interaction with Leptin and Alpha Glucosidase / Roots: Study using in silico molecular docking evaluated the interaction of A. indica compounds with leptin and alpha glucosidase to explore its antihyperglycemic effect. Compounds isolated were repundusinic, mauritanin, hesperetin, acaindinin, and glucogalin in pdb format. Results of docking analysis demonstrated the compounds from Ai roots contain antihyperglycemic-antiobesity activity via inhibition of leptin and alpha glucosidase receptors. (57)
• Antimalarial: Study evaluated extracts of A. indica and C. hirsutus for in vitro antimalarial activity against 3D7 and K1 strains of Plasmodium falciparum. The leaf chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of A. indica showed IC50s of 3.34 µg/ml and 3.71 µg/mL, respectively against 3D7 strain, and IC50s of 1.47 µg/mL and 2.32 µg/mL, respectively against K1 strain. All extracts were non toxic against Vero cell line with CC50 >20 µg/mL. (58)
• Wound Healing / Antioxidant / Fibroblasts Viability / Migration Stimulation / Roots and Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the antioxidant activity of aerial parts and root ethanolic extracts and their effect on fibroblast viability and migration. Aerial parts exhibited higher DPPH scavenging activity compared to the root extract with IC50s of 6t2 µg/,l and 206 µg/ml, respectively. Both showed low toxicity towards fibroblasts. Aerial parts significantly induced fibroblasts proliferation up to 134% with significant wound closure percentage. Results suggest great wound healing potential, with high antioxidant activity and stimulation of fibroblast migration and proliferation. (59)
• Burn Wound Healing Activity / Ointment Formulation: Study evaluated the burn wound healing activity of A. indica in ointment formulation in burns induced with hot iron plates on the back of rabbits. Extract ointment formulations in concentrations of 3, 5, and 7% were applied to the burn wound. Results showed 3% concentration had a slow and low effect; 5% showed a moderate healing phase; and 7% showed best results. (61)
• Nanoparticles / Antibacterial / Larvicidal / Leaves: Study reports on the preparation of herbal nanoparticles from shade dried leaves of A. indica using the ball-milling technique. The NPs were investigated against three disease vectors viz., Aedes aegypti, Anopheles stephensi, and Culex quinquefasciatus, and showed significant larvicidal activity. On antibacterial screening, the magnitude of inhibition was slightly higher in E. coli than S. aureus, 17.51 mm and 16.72 mm, respectively. (62)
• Decreased Neuronal Damage in Hypoxia-Induced Hippocampal Injury / Combination of A. indica and Centella asiatica: About 80-85% of strokes are ischemic and lead to alterations in neuronal cell morphology and cell death. Study evaluated the neurotherapeutic effect of combination of AI-CA extracts in improving hippocampal neuron injury post-hypoxia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Treatment groups were given citicoline 50 mg/kbw and AI-CA combination in doses of 150/150, 200/150, 250/150 mg/kbw. Treatment with citocoline significantly decreased nerve cell damage (30.8%); AI-CA combinations decreased nerve cell damage by 36%, 36.4%, and 30.4%, respectively, compared to control rats (15.4%). The extract combination decreased neuronal damage; the improvement was not significantly different to citicoline. (63)
• Cat Attractants / Roots: The roots of the plant are known to elicit a drug-like effect on cats. Study evaluated if a preparation of roots might be effective in traps to attract feral cats. The volatile nature of attractants made it unviable and impractical to use traps. Evaluation of volatile components emitted by plant roots identified two iridoid compounds: (4R,4aR,7S,7aR)-isodihydronepetalactone and (4R,4aS,7S,7aR)-isoiridomyrmecine, which are known to affect behavioral activity in cats. Study suggests potential application of the compounds in feral cat control and use of the attractants to monitor other felid species around the world in conservation projects. (64)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
Extracts in the cybermarket.
|



 Gen info
Gen info



